Relationship between information and data and interaction process
Source: Shangpin China |
Type: website encyclopedia |
Time: 2015-06-15
Relationship between information and data Another concept that is almost as widely used as information is "data". Data is the original facts about an organization and its business or affairs. The concept of data includes two aspects: first, data content is the reflection or description of the characteristics of things; second, data is a collection of symbols. For example, in order to describe the information of a student, a group of data "05020204, Guan Yu, 1.78, Han nationality, and information technology" can be used to express, This set of data describes the student's student number, name, height, nationality and major, which are collections of numbers or Chinese characters. Here, these symbols have been given specific meanings by people, so they have the function of transmitting information.
From this example, we can see the inherent relationship between information and data: data is the symbolic representation of information, or carrier; Information is the connotation and semantic interpretation of data.
In addition, the specific information and Beijing website production The correspondence between data varies from environment to environment. The same information may have different symbols, and the same data may have different interpretations.
Data can represent information, but not all data can represent information. As people often say: "If the computer inputs garbage, the output will also be garbage." The same data may have different interpretations. It can be seen that information is only the data that people digest and understand. Information is abstract and does not change with the data form determined by the data device, while the data representation is optional.
According to the above description of information and data, the following conclusions can be drawn.
(1) Information and data are inseparable. Data is the carrier of information, and information is contained in data. (2) Information is obtained through data processing and is the product of data processing. (3) Information contains people's subjective consciousness, which exists only for the information receiver. (4) Data itself is objective and has no real value. It is meaningful only after being processed into information. (5) Both information and data record the existence state and characteristics of objective things.
Information transmission and interaction
The process of sending data and information from one place to another is called transmission. For example, the telephone system transmits voice from the calling party to the called party. Computer systems can do exactly the same thing using telephone lines. Computer network can also transmit data and information through satellite, optical fiber and other media.
1. Information transmission process
The transmission of information can be better understood with the help of a simple model shown in Figure 2-2.
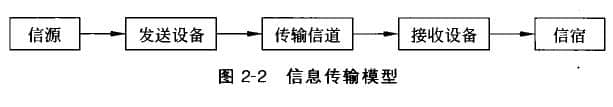 The information transmitted by the information transmission system can be language, text or image. Before the information transmission, the language, text or image must be first transformed into an electrical signal, which is the source of the information.
The signal transmitted from the source is processed by the transmitting device. The transmitting equipment has two main tasks: one is modulation; The second is amplification. Its purpose is to radiate the signal to be transmitted efficiently and remotely, so that it can spread in the transmission channel. The output signal of the transmission equipment is high-frequency modulated signal.
The transmission channel is a signal channel connecting the sending and receiving ends, also called transmission medium. Transmission channels can be divided into two categories: one is wired channels (using wires to transmit electrical signals); The other is wireless channel (using free space to transmit electrical signals in the form of electromagnetic waves). Different channels have different transmission characteristics.
The task of the receiving equipment is to process the modulated signal transmitted from the channel to recover the original signal consistent with the transmission end. This process is demodulation. Due to the attenuation characteristics of the channel, the signal level reached by long-distance transmission is usually very weak, and demodulation can only be performed after amplification. At the same time, there are many interference signals in the channel, so the receiving equipment must also have the ability to select useful signals from many signals and filter out interference signals.
In order to ensure that the destination can accurately understand the encoding method of information from the source without ambiguity, both parties must jointly define a set of information representation methods and meanings. This agreement is called communication protocol.
Information is sent in the form of messages. A group of symbols sent/received at a time constitutes a message, which is generated according to information coding rules.
2. Modulation and demodulation
Modulation is a process in which some parameters (such as amplitude, frequency, phase, etc.) of a signal (such as light, high-frequency electromagnetic wave, etc.) change according to the characteristics of another signal (such as sound, image, etc.) to be transmitted. For example, the signal to be transmitted is "added" to the high-frequency oscillation signal and then transmitted by the antenna. High frequency oscillation signal is a carrier vehicle carrying information, so it is called carrier, and the signal to be transmitted is called modulation signal. According to the different parameters of the modulated high-frequency oscillation signal, the modulation methods are also different.
Let the high-frequency carrier signal be expressed as u c (t)=U cm cosw c t. If the low-frequency signal to be transmitted is used to control the amplitude U of high-frequency carrier cm , so that its amplitude changes with the change of low-frequency signal, it is called amplitude modulation, and the amplitude modulation cup is referred to as AM.
If low-frequency signal is used to change the frequency w of high-frequency signal c , so that its frequency changes with the change of low-frequency signal, it is called frequency modulation, referred to as FM, which is represented by FM. If low-frequency signal is used to change the phase of high-frequency signal so that its phase changes with the change of low-frequency signal, it is called phase modulation, which is represented by PM. The modulated carrier carries the information contained in the modulated signal, which is called modulated signal or modulated wave.
Why modulation? There are three reasons. One is to increase the frequency for radiation. Due to the short transmission distance of low-frequency signals, they will attenuate greatly when encountering obstacles. To transmit directly, the required antenna must be very long. Therefore, low-frequency signals must be radiated by means of high-frequency electromagnetic waves. The second is to realize channel multiplexing and avoid interference between various signals; The third is to improve the system performance and improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the system output.
Demodulation is the reverse process of modulation, that is, the process of restoring low-frequency modulated signals from high-frequency modulated signals. The demodulation process of the amplitude modulated wave is called detection, the demodulation process of the frequency modulated wave is called frequency discrimination, and the demodulation process of the phase modulated wave is called phase discrimination. The selection of modulation mode is comprehensively considered according to the transmission requirements and the characteristics of various modulation modes. For example, the receiving equipment required for amplitude modulation is simple, so it is suitable for radio broadcasting in various medium, short wave and ultra short wave bands, but its anti-interference ability is poor; FM has strong anti-interference ability, but because it occupies a wide frequency band, it is suitable for ultra short wave band, such as television sound, mobile communication, etc.
The information transmitted by the information transmission system can be language, text or image. Before the information transmission, the language, text or image must be first transformed into an electrical signal, which is the source of the information.
The signal transmitted from the source is processed by the transmitting device. The transmitting equipment has two main tasks: one is modulation; The second is amplification. Its purpose is to radiate the signal to be transmitted efficiently and remotely, so that it can spread in the transmission channel. The output signal of the transmission equipment is high-frequency modulated signal.
The transmission channel is a signal channel connecting the sending and receiving ends, also called transmission medium. Transmission channels can be divided into two categories: one is wired channels (using wires to transmit electrical signals); The other is wireless channel (using free space to transmit electrical signals in the form of electromagnetic waves). Different channels have different transmission characteristics.
The task of the receiving equipment is to process the modulated signal transmitted from the channel to recover the original signal consistent with the transmission end. This process is demodulation. Due to the attenuation characteristics of the channel, the signal level reached by long-distance transmission is usually very weak, and demodulation can only be performed after amplification. At the same time, there are many interference signals in the channel, so the receiving equipment must also have the ability to select useful signals from many signals and filter out interference signals.
In order to ensure that the destination can accurately understand the encoding method of information from the source without ambiguity, both parties must jointly define a set of information representation methods and meanings. This agreement is called communication protocol.
Information is sent in the form of messages. A group of symbols sent/received at a time constitutes a message, which is generated according to information coding rules.
2. Modulation and demodulation
Modulation is a process in which some parameters (such as amplitude, frequency, phase, etc.) of a signal (such as light, high-frequency electromagnetic wave, etc.) change according to the characteristics of another signal (such as sound, image, etc.) to be transmitted. For example, the signal to be transmitted is "added" to the high-frequency oscillation signal and then transmitted by the antenna. High frequency oscillation signal is a carrier vehicle carrying information, so it is called carrier, and the signal to be transmitted is called modulation signal. According to the different parameters of the modulated high-frequency oscillation signal, the modulation methods are also different.
Let the high-frequency carrier signal be expressed as u c (t)=U cm cosw c t. If the low-frequency signal to be transmitted is used to control the amplitude U of high-frequency carrier cm , so that its amplitude changes with the change of low-frequency signal, it is called amplitude modulation, and the amplitude modulation cup is referred to as AM.
If low-frequency signal is used to change the frequency w of high-frequency signal c , so that its frequency changes with the change of low-frequency signal, it is called frequency modulation, referred to as FM, which is represented by FM. If low-frequency signal is used to change the phase of high-frequency signal so that its phase changes with the change of low-frequency signal, it is called phase modulation, which is represented by PM. The modulated carrier carries the information contained in the modulated signal, which is called modulated signal or modulated wave.
Why modulation? There are three reasons. One is to increase the frequency for radiation. Due to the short transmission distance of low-frequency signals, they will attenuate greatly when encountering obstacles. To transmit directly, the required antenna must be very long. Therefore, low-frequency signals must be radiated by means of high-frequency electromagnetic waves. The second is to realize channel multiplexing and avoid interference between various signals; The third is to improve the system performance and improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the system output.
Demodulation is the reverse process of modulation, that is, the process of restoring low-frequency modulated signals from high-frequency modulated signals. The demodulation process of the amplitude modulated wave is called detection, the demodulation process of the frequency modulated wave is called frequency discrimination, and the demodulation process of the phase modulated wave is called phase discrimination. The selection of modulation mode is comprehensively considered according to the transmission requirements and the characteristics of various modulation modes. For example, the receiving equipment required for amplitude modulation is simple, so it is suitable for radio broadcasting in various medium, short wave and ultra short wave bands, but its anti-interference ability is poor; FM has strong anti-interference ability, but because it occupies a wide frequency band, it is suitable for ultra short wave band, such as television sound, mobile communication, etc.
Source Statement: This article is original or edited by Shangpin China's editors. If it needs to be reproduced, please indicate that it is from Shangpin China. The above contents (including pictures and words) are from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us in time (010-60259772).