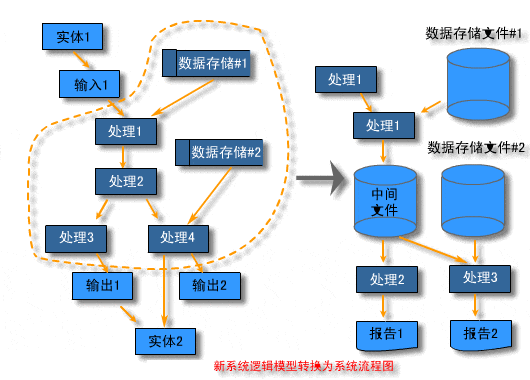
What is an information system
Source: Shangpin China |
Type: website encyclopedia |
Time: 2015-06-15
Information Systems are man-made systems used by one or more people to help people complete specific tasks. The shape and scale of information systems are arbitrary. Information system is a system mainly for processing information. It is composed of people, hardware, software and data resources. The purpose is to collect, process, store, transmit and provide information in a timely and accurate manner. In fact, there are different kinds of information systems. Each type of information system is built to meet the needs of different types of users, providing users with Marketing website construction Services. Different kinds of information systems also need specific tools, technologies and methods when developing.
1. Transaction processing system
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) represents one of the most popular and oldest information systems of T. Enterprise transactions are events that serve enterprise tasks. These transactions are the main ways for enterprises to deal with their suppliers, customers, partners, employees and governments. Transaction processing system is an information system that collects and processes data about enterprise transactions.
A transaction is an event that directly serves enterprise tasks or is valuable to the organization. This event can be internal or external. Examples of transactions include purchase, order, sales, appointment, registration, receipt, delivery, invoicing, and payment.
The transaction processing system can respond to transactions (such as orders, clocking, or payments) and initiate transactions (such as invoicing, checking, or invoicing), or both. In addition, the transaction processing system can respond to both external events (such as processing orders from customers) and internal events (such as generating product orders for enterprises).
Another function of the transaction processing system is data maintenance, which provides the administrator with the ability to modify stored data. For example, the system must provide the function of adding and deleting "customers" and "products", as well as the function of modifying specific data. The design of transaction processing system is more concerned with response time, throughput, correctness, consistency and service. Although most transaction processing systems have been computerized for some time, the trend of Business Process Redesign (BPR) is still bringing new opportunities for improvement.
Business process reengineering refers to the research, analysis and redesign of the basic business processes of enterprises to reduce costs and (or) improve efficiency.
In many cases, the existing system only automates outdated enterprise practices, inefficient strategies and bureaucracy. When enterprises reconstruct these processes and practices, the underlying transaction processing system must also be reconstructed. There are still many new opportunities to develop transaction processing systems.
2. Management information system
Management Information Systems (MIS) is a supplement to the transaction processing system. It receives raw data from the transaction processing system and converts these data into meaningful reports or graphs to support managers in enterprise planning and control.
Management information system is an information system application that can provide management oriented reports. These reports are generally generated according to the preset plan and displayed in the preset format.
The management information system can display detailed information, summary information and exception information. The detailed information is used for operation management and meets the needs of system management (such as government requirements); Summarize information and combine original data to quickly indicate development trends and possible problems; Exception information filters data according to certain rules or standards, and reports exceptions (for example, only those goods with too little inventory). As long as organizations still consider information as an important management resource, opportunities for developing management information systems will continue to increase.
3. Decision support system
Decision Support Systems (DSS) is a special kind of information system, which provides support for the decision-making process. When used by senior managers, these systems are sometimes called Executive Information Systems (EIS).
Decision support systems generally do not make decisions or solve problems, and decisions are still made by people. Decision support systems focus on providing necessary help and support for decision makers in the process of making decisions. Decision support systems are often designed to support unstructured decisions, that is, those decisions whose results are unpredictable.
This may seem impossible, but it is not. DSS is based on the reality that transaction processing systems and management information systems have collected the data needed for unstructured decision-making. DSS also provides decision makers with tools to access, analyze these data and make decisions. In general, DSS provides decision makers with the following types of support:
- Identify problems or decision-making opportunities (similar to exception reports);
- Determine possible solutions;
- Access to information needed to solve problems or make decisions;
- Analysis of possible decisions or variable factors affecting decisions, sometimes referred to as What it analysis;
- Simulate possible schemes and possible results after adopting these schemes.
DSS tools include spreadsheet software, database management system, customized report tools and statistical analysis programs.
4. Expert system
Expert Systems (ES) is an extension of decision support systems.
Expert system is a programmed decision-making information system, which collects and reproduces the knowledge and experience of professional problem solvers or decision makers, and then simulates experts to "think" and "act".
An important requirement of expert system is to copy the professional knowledge of experienced managers, professionals and technicians. These experts usually have knowledge and experience, and these knowledge and experience are difficult to copy or replace in all organizations. The expert system simulates the logical reasoning of experts in their corresponding fields.
The expert system is realized by using artificial intelligence (Al) technology. Al technology collects and stores expert reasoning knowledge and provides access to expert reasoning knowledge. Expert systems also need data and information from other similar information systems, but they require the storage of rules (called heuristic rules) that simulate the reasoning process of experts using data and information, which is unique.
5. Office automation system
First of all, office automation is not just the application of word processing software and electronic forms.
Office Automation Systems (OAS) and Workgroup Management Systems (WMS) support a wide range of enterprise office activities. They provide improved workflow and communication among staff, regardless of whether they are in the same office or not.
The office automation system provides all relevant information for people who need information. The functions of the office automation system include word processing, spreadsheet, graphic display and desktop publishing, electronic planning and resource allocation, as well as some commonly used communication methods, such as e-mail, voice mail, video conference, etc. The core of the office automation system is to transmit relevant information to those who want it at an appropriate time.
The groupware management system comes into being with the development of modern enterprises. It extends the ability of traditional office automation systems. The groupware management system includes collaboration technologies, such as Lotus Notes.
6. Web based system
Web Based Systems (WBS) is a kind of information system with the rapid development of the Internet. This kind of system is no longer a simple page plus hyperlinks of several other websites. Web based systems support the complex environment of business activities on the Internet, and the applications in this field are endless at present. Web based applications include B2B/B2C e-commerce, data management, customer relationship management, supply chain management, and enterprise resource management.
Source Statement: This article is original or edited by Shangpin China's editors. If it needs to be reproduced, please indicate that it is from Shangpin China. The above contents (including pictures and words) are from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us in time (010-60259772).