Innovative networking services and applications
Source: Shangpin China |
Type: website encyclopedia |
Time: 2015-06-17
1. Cloud computing Cloud Computing uses large-scale data centers or supercomputer clusters to connect computer hardware and Website production System software and other resources are provided to users in the form of free or on-demand payment, and applications are provided in the form of services. Such services are called "software as a service".
The hardware and software resources of data centers or supercomputer clusters are called "clouds". "Cloud" is called "Public Cloud" if it is open to the public in the form of pay as you go, and the service sold is called "Utility Computing" or "Utility Computing". If the "cloud" consists of a data center used internally by a company and is not disclosed to the public, it is called a "private cloud". Therefore, "cloud computing" is composed of SaaS and utility computing, excluding private clouds. People can be users or providers of SaaS or utility computing.
The word "cloud" of cloud computing is borrowed from the telephone system. In the past, data was transmitted on the lines connected by cables. In the 1990s, long-distance telephone companies began to provide data transmission services with Virtual Private Network (VPN), maintaining the original bandwidth and lower costs. With VPN, the specific transmission line cannot be known accurately in advance, so this type of networking is called "Telecom Cloud". Cloud computing is similar. The servers in the data center mainly rely on virtualization technology to meet the needs of users. It is difficult to determine how many virtual hosts there are at a specific time in advance.
Cloud computing users can make requests and get services through browsers, and can process business in the mobile process. The computing resources used are operated by a third party in the data center owned by a third party. Users need not care about the equipment and technology used. Some vendors also provide a way for users to add functions instantly through remote interfaces or Web browsers.
Cloud computing requires automation of management. If a system allocates resources through human management, it is not cloud computing, but a data center. Cloud service is a web service provided through cloud computing, but the application of cloud computing is not limited to web services, but also includes storage, ordinary computing or any number of specialized services. With cloud computing, people only need to pay according to the actual resources and time used, adjust computing capacity as needed, and adapt to changing workloads and business needs.
With the reduction of interconnection cost, the development of processor multi-core architecture and its inherent parallelism, cloud computing is strongly supported and its applications are expanding rapidly.
2. Pervasive computing The concept of pervasive computing was put forward by Mark Weiser when he was the chief technical officer of Xerox's Palo Alto Research Center around 1988. At that time, it was called Ub Late uitous Computing. With the emergence of small information terminals represented by mobile phones and the popularity of the Internet, in 1999, IBM began to develop real-time, low-power A pervasive computing system with large bandwidth, which is represented by Pervasive Computing. Now Ubiquitous Computing and Pervasive Computing have become synonyms, which are collectively called "pervasive computing" in Chinese.
Pervasive computing is a field of rapid development of information and communication technology (ICT). It integrates ICT into people's daily life and environment, and enables microprocessors to have built-in communication capabilities. Pervasive computing systems (PCs) and their services introduce more user knowledge about the environment, enabling users to have more control over the environment, no matter where they are.
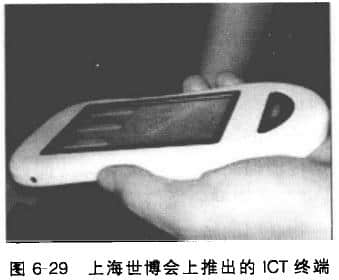
Let's take a look at an example - the ICT terminal in the Shanghai World Expo Information and Communication Museum. During the 2010 Shanghai World Expo, each visitor to the Information and Communication Pavilion can temporarily borrow a new handheld personal information and communication mobile device, as shown in Figure 6-29. This equipment is the first in the history of the World Expo. The whole system integrates intelligent wireless equipment, fast charging system, communication and network tracking, radio frequency identification and exhibition control system. With this information and communication equipment, tourists can create their personalized "dream" files to participate in the exhibition, collect dreams, win prizes, interact with exhibition items, and learn more about the exhibition. These personalized content will be collected for tourists to download from the online exhibition hall. Pervasive computing technology includes three main aspects: computing equipment Communication connection and user interface.
(1) Computing devices. Computing devices come in many forms and vary in size. From handheld devices (such as mobile phones) to small embedded devices, they can communicate with each other and have certain intelligence. Computing devices are divided into three categories: sensors, processors, and actuators. Sensors are input devices that detect changes in the environment, user behavior, and human commands, The processor is an electronic device that interprets and analyzes data, and the exciter is an output device that responds to the processed information and changes the environment through electronic or mechanical methods.
Pervasive computing emphasizes the use of mobile technology, geographic location systems and the Internet to connect databases, and the distribution of information through personal digital devices.
(2) Communication connection. Pervasive computing relies on independent electronic devices to form an interconnected network, which can be effectively connected through wired or wireless networking technology. The effectiveness of pervasive computing systems depends on the interoperability achieved by interconnection and the integration of wired and wireless technology standards.
(3) User interface. Pervasive computing needs new user interfaces, which can sense and provide more information about users and environment to processors. The input of the user interface should be visual information (such as face recognition, posture recognition), sound, smell or touch recognition, and other perceptible information, such as temperature. The output should also be like this. Interface technology can also tailor information to meet specific needs, and may also require adaptation to unpredictable situations, which is a greater challenge.
3. Rich Internet applications For a long time, desktop applications have smooth user interaction. Because all processing is carried out on the user's machine, it can provide a more seamless user experience. However, software is sold, and there will be problems with release and update. In addition, Web applications are easy to obtain from the Internet. They can get rid of the problems of software release and update, but they are poor in user interaction experience.
The Web based business environment is changing towards an Experience Oriented model, so the work of developers must create a positive and unforgettable experience for customers, that is, Web sites provide intuitive views to enable customers to understand products as much as possible. Rich Internet Application (RIA) is a new type of Web applications that is changing in this direction, It has better response and interaction ability than traditional HTML Web applications. It combines the direct interaction of desktop applications and the distribution ability of Web applications.
RIA uses the computing power of the client to improve the interaction with customers. Internet standards are constantly evolving to adapt to this new technology. The original page update is to download a new page, while RIA allows changes to individual content on the page. Other information, such as error messages and confirmation messages, can be displayed on the page to provide immediate feedback instead of opening another page.
4. Internet of Things The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network that connects any item to the Internet for information exchange and communication in accordance with the agreed protocol through radio frequency identification, infrared sensors, global positioning systems, laser scanners and other information sensing devices to achieve intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, monitoring and management. The Internet of Things is the "Internet of Things". This has two meanings: first, the core and foundation of the Internet of Things is still the Internet, which is an extension and expansion of the Internet; Second, its user end extends to any item.
The "things" here can be included in the scope of the "Internet of Things" only if they meet the following conditions: receivers with corresponding information; There is a data transmission path; It has certain storage function; With processor; Operating system; There are special applications; With data transmitter; Follow the communication protocol of the Internet of Things; There is a unique number that can be identified in the actual network.
The concept of the Internet of Things was put forward in 1999. On November 17, 2005, at the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) held in Tunisia, the International Telecommunication Union released the ITU Internet Report 2005: the Internet of Things, which formally put forward the concept of "the Internet of Things". The report pointed out that everything is here. The Internet of Things communication era is coming, and all objects in the world - from tires to toothbrushes From houses to paper towels can be actively exchanged through the Internet. RFID technology, sensor technology, nanotechnology, and intelligent embedded technology will be more widely used. A report of the International Telecommunication Union once described the scene of the "Internet of Things" era: when the driver makes a mistake, the car will automatically alarm; The briefcase will remind the owner of what he forgot; The clothes will "tell" the washing machine's requirements for color and water temperature; wait.
The Internet of Things makes full use of the new generation of information technology in all walks of life. Specifically, sensors are embedded and equipped in power grids, railways, bridges, tunnels, roads, buildings, water supply systems, dams, oil and gas pipelines and other objects, and then the "Internet of Things" is integrated with the existing Internet to achieve the integration of human society and physical systems. In this integrated network, there is a super powerful central computer cluster that can manage and control the people, machines, equipment and infrastructure in the integrated network in real time. On this basis, people can manage production and life in a more refined and dynamic way to achieve a "smart" state, improve resource utilization and productivity, and improve the relationship between man and nature.
Source Statement: This article is original or edited by Shangpin China's editors. If it needs to be reproduced, please indicate that it is from Shangpin China. The above contents (including pictures and words) are from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us in time (010-60259772).