Data transmission technology
Source: Shangpin China |
Type: website encyclopedia |
Time: June 23, 2014
Data transmission technology is closely related to the bandwidth of communication media and the control mode of signal transmission.
1. Baseband transmission, broadband transmission and band transmission
In network communication, it can be divided into baseband transmission and broadband transmission according to the bandwidth of its transmission medium. In order to effectively use the bandwidth and communication capability of the communication medium, Website construction Digital signals can also be modulated to a certain frequency band for transmission. Therefore, another data transmission mode is called frequency band transmission.
1) Baseband transmission
The baseband is the basic frequency band, which is the inherent frequency band of the electrical signal after data coding. It is called the basic frequency band, or baseband for short. To be transmitted by baseband Website construction outsourcing Information (such as 0,1 digits) is called baseband signal.
Baseband transmission means that the baseband signal is transmitted directly on the communication medium without any modulation, which will occupy all the bandwidth of the channel. In baseband transmission, only one kind of signal is transmitted on the whole channel, which can be digital signal or analog signal, but it is usually digital signal. Because of its low channel utilization, this transmission mode is generally suitable for data transmission systems with short distance and little signal power attenuation. For example, in LAN communication, baseband transmission technology is used.
2) Band transmission
The frequency band is the frequency range between the highest frequency and the lowest frequency of the signal allowed to be transmitted. Band transmission is the transmission of the original signal converted (modulated) into a band signal with a higher frequency range. In the long-distance communication of computer network, the frequency band transmission is usually used instead of baseband transmission. Because the baseband signal has a wide frequency band and low frequency spectrum component, it has poor anti-interference ability and low channel utilization. The frequency band transmission can not only realize the long-distance data transmission, but also realize the multiplexing of the channel, which not only improves the transmission rate of the channel but also improves the utilization rate of the channel.
3) Broadband transmission
In fact, broadband is not strictly defined. In the early days, it was defined as "narrowband" based on the maximum dial-up speed of 56kbps, and "broadband" refers to the Internet access mode of 56kbps and below, and "broadband" refers to the access mode of 56kbps and above. From a cognitive perspective, broadband is the bandwidth that can meet the needs of various media to transmit books on the network. Therefore, broadband is a dynamic and developing concept. With the development of network technology, in order to meet the transmission of a large number of voice, image and other information, the current understanding of broadband is that the transmission rate is above 512kbps or higher. For example, ISDN used to be broadband, but now ISDN is far from meeting today's broadband requirements, so it has long since retired from the ranks of broadband. Broadband transmission is to divide the channel into several sub channels to transmit audio, video and digital signals, etc. Such channel transmission is called broadband transmission.
In the broadband transmission system, the channel bandwidth is divided into two or more subchannels with the help of frequency band transmission technology, and each subchannel can transmit data signals in different frequency ranges. For example, ADSL and Cable adopt broadband transmission technology.
[Example] ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) is a new broadband data transmission mode. Because its uplink and downlink bandwidth is asymmetric, it is called asymmetric digital subscriber line loop. Its data transmission mode uses frequency division multiplexing technology to divide ordinary telephone lines into three relatively independent channels (channels), namely, telephone voice signal, uplink digital signal and downlink digital signal. Through the frequency band transmission technology, the respective communication signals are modulated to the corresponding channels for transmission, which not only avoids the interference between the transmission of various signals, but also achieves the goal of making phone calls and surfing the Internet, It also makes full use of the communication ability of the line.
2. Asynchronous transmission and synchronous transmission
In the process of network communication, when the sender sends data, the receiver must know exactly when to start receiving and processing data. Only when the sender and receiver coordinate with each other can the correct transmission of data be ensured. Therefore, there are two transmission modes, namely asynchronous transmission and synchronous transmission.
1) Asynchronous transmission
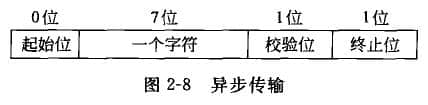
The bit stream packet of asynchronous transmission transmission data is based on characters. The start bit (i.e. synchronous information) is sent before each character is transmitted, and the end bit is also sent after the transmission. As shown in Figure 2-8, the start bit can be represented by a low level (corresponding to 0), and the stop bit can be represented by a high level (corresponding to 1), marking the start and end of a character transmission, and thus realizing synchronous control of data transmission. After receiving the start bit signal, the receiver can accurately receive the information of a character within the transmission time of 8 -- 11 bits. The stop bit tells the receiver that the character transmission is over. When there is no character transmission, the stop bit is transmitted continuously, and the receiver can identify the start bit of the next character. The purpose of adding parity bit is to check the errors in transmission, and parity check is generally used.
In asynchronous transmission, there is no limit on the time interval between characters (from the end of one character to the beginning of the next character), so the transmission between characters is asynchronous, so this transmission mode is called asynchronous transmission. It is not suitable for transferring large data, such as disk files.
2) Synchronous transmission
The bit stream packet of synchronous transmission data is much larger than that of asynchronous transmission. Unlike asynchronous transmission, which sends each character independently and each character has its own start bit and end bit, it transmits a group of data at a time.
As shown in Figure 2-9, the sender sends a string of synchronous characters SYN (such as 0010110) before sending data. As long as the receiver detects SYN, it is confirmed that it has entered the synchronization state and can receive data. Then both parties will transmit data at the same working frequency until the data transmission is completed and the end sign of the data is received. It can be seen that synchronous transmission has higher transmission efficiency.
3) Comparison between asynchronous and synchronous transmission modes
The advantages of asynchronous transmission are simple, reliable, and suitable for character oriented, low-speed asynchronous communication occasions. It is relatively easy to implement, and the corresponding equipment is also simple and cheap. For example, the keyboard used for input equipment and the communication between computer and Modem are in this way. The disadvantage is that the communication overhead is large, and "synchronization" information needs to be added for each character transmitted. The communication efficiency is relatively low.
Synchronous transmission is much faster than asynchronous transmission because the sender does not have to start and stop every character, and the cost of synchronous transmission is reduced. However, the longer the bit size of the data group, the larger the space required to cache the data, and the longer it will occupy the continuous time of the transmission medium. Therefore, the synchronous transmission mode has certain restrictions on the size of the data group. This synchronous transmission technology is used in the data transmission of LAN.
[Q&A] The cost of synchronous and asynchronous transmission.
In synchronous transmission, a typical data frame may contain 500 symbols (1B=8b, that is, 500 X 8=400 bits) of data, which may only contain 100 bits of overhead. At this time, the increased bit overhead will increase the total number of transmitted bits by 2.5%. If it is transmitted in asynchronous transmission, every 8 bits will increase 2 bit overhead, and the total transmission load will increase by 25%, It is much higher than synchronous transmission.
Source Statement: This article is original or edited by Shangpin China's editors. If it needs to be reproduced, please indicate that it is from Shangpin China. The above contents (including pictures and words) are from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us in time (010-60259772).